Graphene nanotubes for non-marking solid tires: compliance with electrostatic requirements and maintained mechanical properties


The accumulation of static electricity in non-marking tires can lead to an injury to the operator, fire, and damage to the object.
That is why industrial areas are very strictly regulated by ATEX regulations and by the EN 1755 standard, with the latter being specifically related to industrial trucks (including their tires) when working in potentially explosive atmospheres to prevent electrostatic discharges.
According to these standards, this type of product must be anti-static or conductive.
| ATEX 2014/34/EU | EN 1755:2015 | ISO 3691-1:2011 |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres | Safety of industrial trucks. Operation in potentially explosive atmospheres. Use inflammable gas, vapor, mist and dust | Industrial trucks. Safety requirements and verification |
New electrostatic requirements
EN 1755:2015
Mandatory: November 2017
- Static now considered an ignition risk during ‘normal’ operations
- More detailed assessment of non-electrical components is now required
Electrical properties:
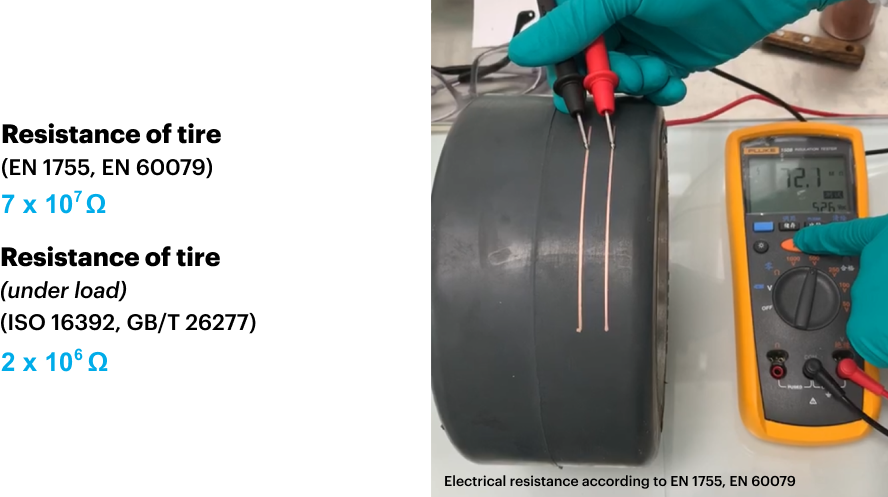
- Surface resistance of 109 Ω
Industries affected:
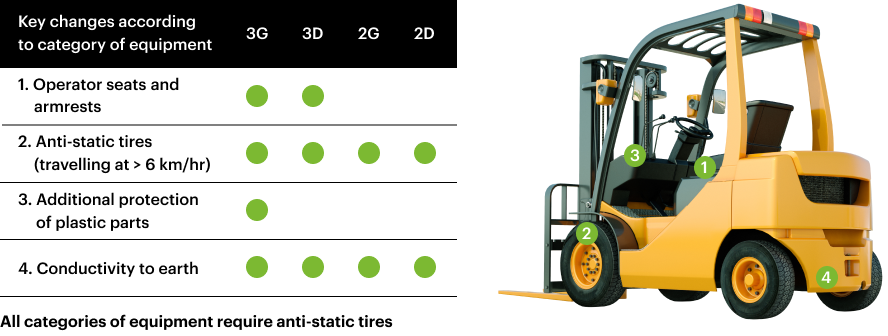
TUBALL™ graphene nanotubes improve the physical and mechanical properties of rubbers, contribute to the required anti-static properties without carbon release, and fully comply with ATEX and EN requirements for ESD protection.
TUBALL™ nanotubes are applied via an easy-to-use additive, TUBALL™ MATRIX, which is a line concentrates based on polymer and plasticizer carriers and pre-dispersed TUBALL™ graphene nanotubes.
TUBALL™ MATRIX for solid tires
|
PROPERTY |
MATRIX 620.3 beta |
|
Compatible formulations |
NR- or NR/BR-based formulations containing mineral fillers |
|
Concentrate carrier |
Polymer in oil-based plasticizer |
|
TUBALL™ GNT content, wt.% |
8.5% |
|
Processing |
Not sensitive |
|
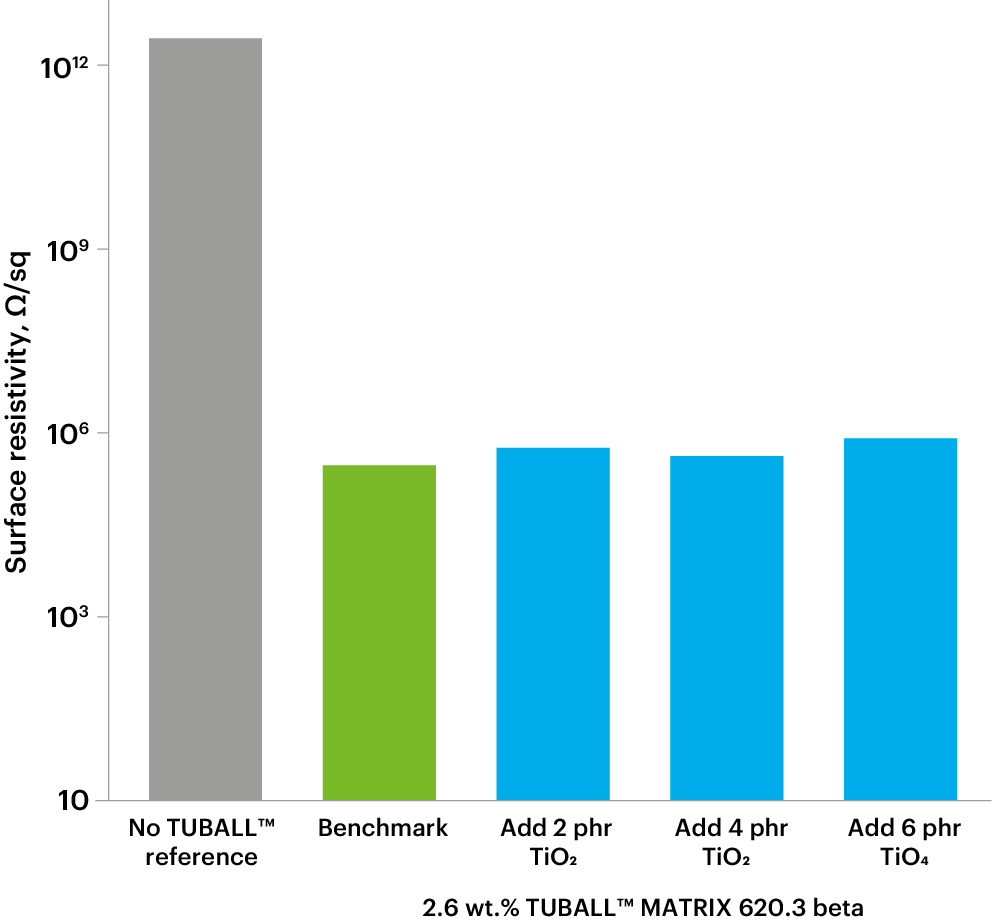
The dosage required for anti-static properties (105–107 Ω) |
From 2.6 wt.% (0.22% TUBALL™) |
|
Mechanical properties |
Not affected |
|
Electrical resistivity |
Stable |
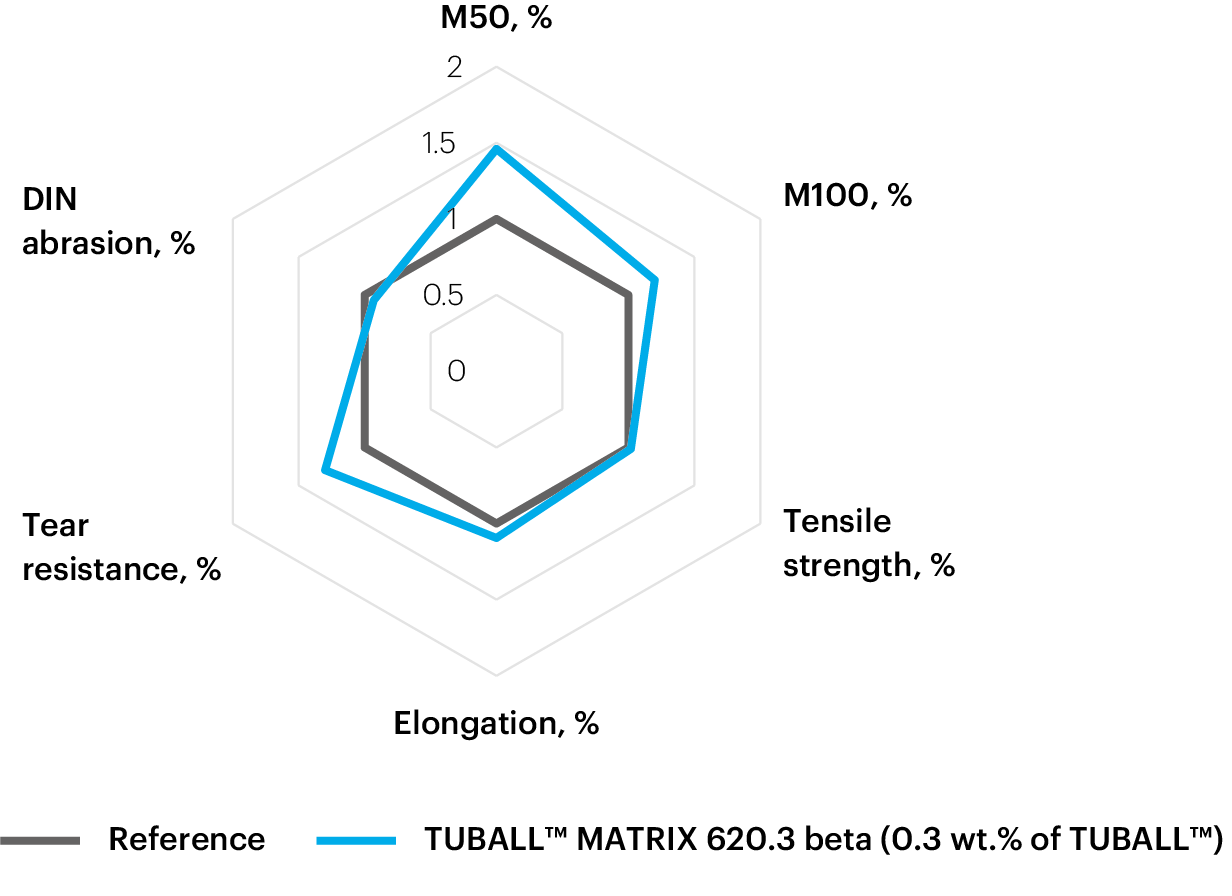
TUBALL™ graphene nanotubes: good performance on all key parameters
In contrast to other conductive agents, TUBALL™ graphene nanotubes are a versatile conductive agent offering good performance on all key parameters.
Test results: mechanical properties
Stable electrical resistivity
Anti-static properties without carbon release, for non-marking colored compounds
RESULTS FOR A MOLDED TIRE
When using carbon black, owing to its high concentration (10% or more) and because of the spherical shape of the particles, a phenomenon is known in the industry as “carbon release” takes place, when the conductive additive is present on the surface of the sample.
In contrast, graphene nanotubes, owing to their much greater length-to-diameter ratio, are not released to the surface.
Marking and non-marking conductive rubbers: How to avoid mistakes
In situations where it is necessary to use non-marking tires, it has been impossible to add any carbon-based fillers – only alternative compositions with a high mineral content have been suitable. Therefore, anti-static plasticizer has very often been used for this purpose in the industry.
A conductive plasticizer is a humidity-dependent material, so it is not stable during use.
To achieve anti-static properties, a high dosage of conductive plasticizer is required. However, this has a negative effect on the physical and mechanical properties, especially the mechanical modulus and tensile stretching. In addition, the plasticizer has a propensity to migrate to the surface during storage and use.
Degradation of mechanical properties and migration of the additive to the surface negatively affect the performance and the shelf life of the product.
Standard processing and mixing equipment
The optimal mixing option is a combination of an internal mixer and a 2-roll mill.
Other benefits
- Maintained elasticity and mechanical properties
- Extra-low dosage of TUBALL™ MATRIX that preserves properties
- Retain colors
- Permanent and uniform electrical conductivity
Please, pay close attention to processing guidelines for TUBALL™ MATRIX 620 & 620.3 beta for non-marking anti-static compounds
Download PDF version:
Application case

NR/BR non-marking solid tires
Additional resources:
Non-marking solid tires: add nanotubes to meet ESD standards
Electrical resistivity guideline: measurement, standards & troubleshooting
Graphene Nanotubes Enable Creation of Non-Marking Anti-Static Tires
Graphene key to non-marking anti-static tires
Contact us to discuss your project specifications or to request a TUBALL™ MATRIX sample